In any computer connection, you should probably decide on a topology.
A web link topology is the physical architecture of how the computers connect to each other.
A classic online grid topology is the Ring Topology.

In this structure, all devices in the web link are connected in a single ring.
All web connection traffic goes in a single direction around the loop.
The concept gets even easier to implement with rack servers.
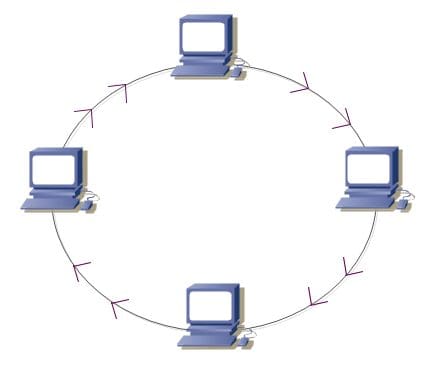
No central server or router is needed to manage the connectivity between devices.
This wastes bandwidth, which may cause issues in heavily loaded networks.
Any single equipment failure can bring down the entire loop.
This issue can be mostly resolved with a bi-directional loop or counter-rotating ring topology variant discussed below.
Making any adjustment to the ring causes a disruption, temporarily breaking the whole ring.
Unfortunately, this also means that all devices need to remain powered on.
If a computer is turned off, its online grid card no longer transmits messages.
This would break the ring, making ring topologies unsuitable for networks that dont have near-perfect up times.
Communication latency is directly proportional to the number of devices in the loop.
Typically, this secondary loop is not used unless the main loop is broken.
Theoretically, a secondary loop could also be used to provide extra bandwidth, though this generally isnt done.
Instead, bi-directional communication over a single cable is enabled by utilising full duplex communication.
This helps to provide fault tolerance in a loop but doesnt address complexities of scale or the latency issue.
A token ring topology may be easy to confuse with ring topology, however, they are very different.
Despite the name, a token ring data pipe actually uses a star topology at the physical connectivity layer.
Conclusion
Ring topology is a computer data pipe architecture that places all devices in a single ring.
For these reasons, ring topologies are now very rarely used, if at all.
Star topology networks tend to be used for endpoints, while backend networks use a mesh topology.