NAND or a NAND gate is a term found in digital electronics.
It refers to a logic gate that produces a specific result.
NAND itself is short for Not-And.
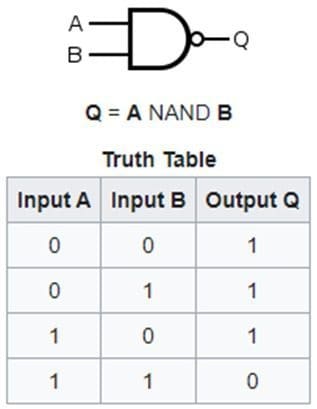
So, if 0 and 0, or 0 and 1 are put in, the output is 1.
Only if the input is 1 and 1 does the NAND gate return a 0.
Tip:The inputs and outputs are sometimes considered high and low rather than true or false.

Naturally, Low is 0, and High is 1.
Its functionally irrelevant what they are called the important parts are the values of 0 and 1.
The standard setups are 2-, 3-, 4 and 8-input gates.
These versions are actively used in semiconductors available on the market.
They can be used to express absolutely any Boolean function if they are combined correctly.
A Boolean function is a function that is based on two values once again, 0 and 1.
Boolean functions and logic gates like NAND or NOR are essential in working various computer parts.
You could build an entire computer processor from nothing but NAND gates.
In this case, it means a mathematical function proven in 1913 by Henry Sheffer.
All combinations other than all 1s return a 1 and all 1 inputs return 0 as an output.
As mentioned, this functional completeness means that NAND logic is enough to build any other logic gate.
This is done by repeating using multiple NAND gates in specific configurations.
One of the more complicated possible Boolean functions is XNOR.
Conclusion
NAND is a logic gate; it stands for Not-And.
A NAND gate is the logical inverse of an AND gate.
An AND gate only returns true if all inputs are true.
Conversely, a NAND gate is always true unless all inputs are true.
NAND gates are core components of processors as well as flash memory.