Google Safe Browsing is a service that allows developers and browsers to test whether a URLcontains malwareor phishing content.
The service relies on a list of URLs that are regularly updated based on data collected from users.
Contents
How Does Google Safe Browsing Work?

To use Safe Browsing, Chrome saves a series of mandatory cookies on your machine.
If any matches are found, youll get an alert.
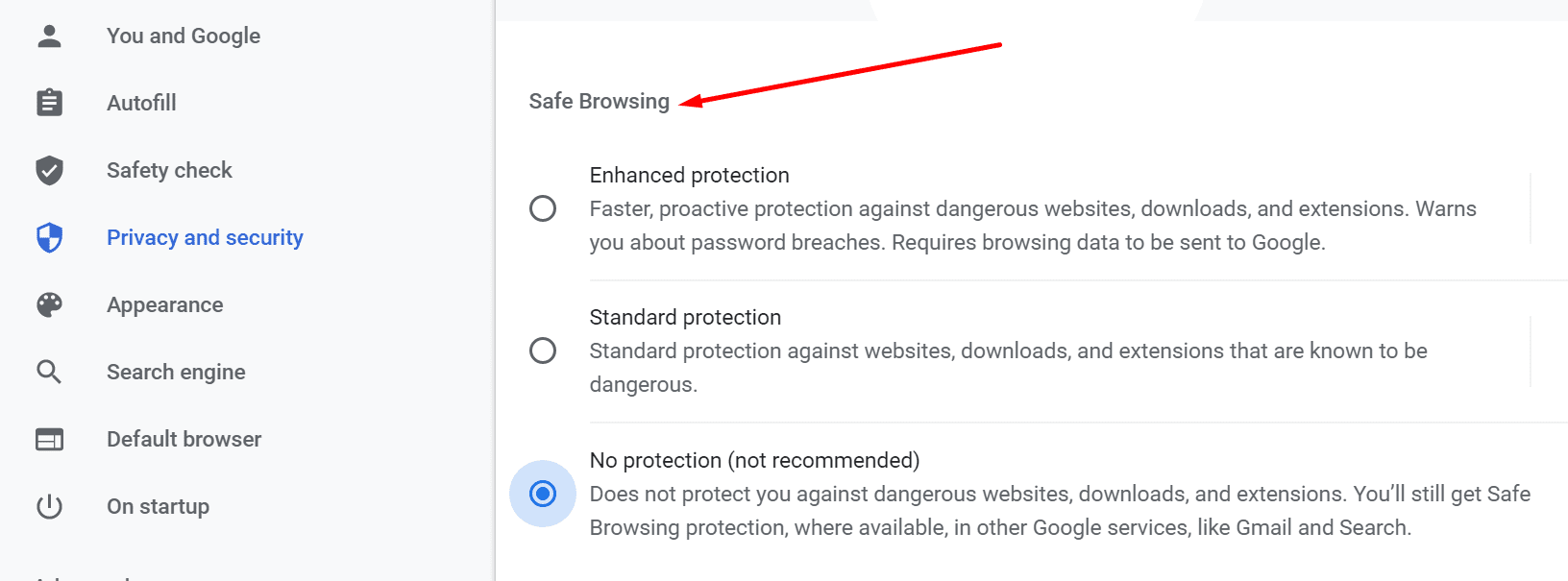
Each level brings its own specific security features.

Of course, if you dont want to take any risks, enable Enhanced Protection.
Safe Browsing Enhanced Protection
This level offers proactive protection against malicious websites.
In other words, Chrome will nip threats in the bud.
Or as Google says:
Predicts and warns you about dangerous events before they happen.
Youll receive alerts about potentially unsafe webpages, download files, and extensions.
Youll also get alerts about password breaches.
If you enable this option, keep in mind that Chrome will send your browsing data to Google.
As Google explains:
Sends URLs to Safe Browsing to check them.
Temporarily links this data to your Google Account when youre signed in, to protect you across Google apps.
If you want to learn more about Enhanced Safe Browsing Protection in Chrome, check outthis blog postfrom Google.
So, theres no direct connection to Safe Browsings servers for now.
you’ve got the option to enable a series of additional options, including alerts about password breaches.
No Protection
By checking this option, you basically turn off Safe Browsing.
your system wont be protected against malicious websites.
And Chrome wont alert you about any cyber-threats.
We dont recommend disabling Safe Browsing.
If youre worried about your browsing data being sent to Google, you could enable Standard Protection.
Safe Browsing Lookup API
Google also maintains the Safe Browsing Lookup API.
Developers can use this security protocol to check URLs against Googles lists of unsafe webpages.
Many users expressed their privacy concerns in regards to the Lookup API.
This is because the protocol does not hash the URLs to be analyzed.
As a result, the server knows what URLs API users have analyzed.
Chrome uses the Safe Browsing Update API.
This tool downloads an encrypted list of URLs (32-bit hash prefixes) on your setup.
So when your internet tool checks an URL, the server doesnt know what website is analyzed.
Google cannot determine the complete URL based only on a partial URLfingerprint.
If you want to learn more about the Safe Browsing API, check outthis support pagefrom Google Developers.