The CPU is often thought of as the brain or heart of a computer.
The motherboard forms the backbone of the computer.
Most PC components connect directly to the motherboard, with everything else connecting to it indirectly.
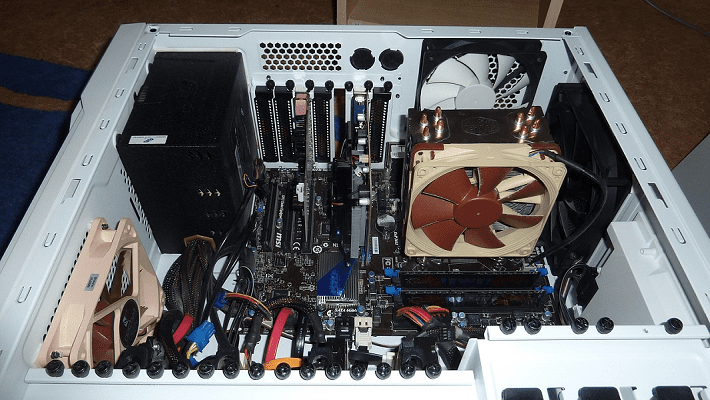
The chipset controls connectivity to peripherals and storage.
PCIe slots offer ultrahigh-speed connectivity for add-in cards.
Rear panel connectors provide connectivity options.

Power connectors are also critical, taking power directly from the PSU and distributing it to all other components.
Some devices that connect to the rear panel connectors may also be directly connected.
For example, USB online grid cards and storage.
Many devices connect to the motherboard via cables.
These include SATA storage drives, case and radiator fans, and addressable RGB lighting.
The last set of devices connects entirely secondarily.

There are many different connectors on a motherboard.
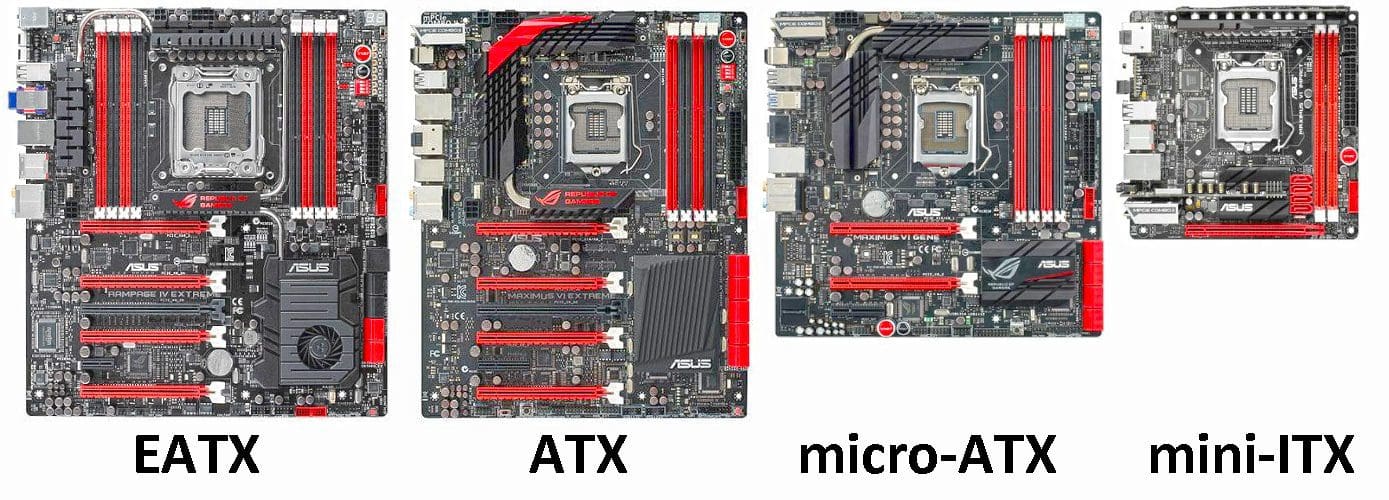
There are some motherboards that are designed to have all the bells and whistles.
These are obviously expensive and large.
This means a large case is required.
The large case and the abundant connectivity, however, means that theres very little limitation on component selection.
These are small form factor computers.
Because of the size constraints of small form factor cases, cooling options are often more limited.
They are designed to fit in exactly one jot down of socket.
To allow easy drop-in CPU upgrades, AMD has opted to rarely upgrade its CPU socket.
The issue with this is that each generation of processors comes with a new chipset.
The chipset affects the connectivity that the motherboard can offer.
Intel goes the opposite way from AMD.
It updates the CPU socket every two generations.
This almost certainly means you should probably buy a new motherboardandCPU if you want to upgrade.
It does, however, mean you tend to get all of the latest features supported.
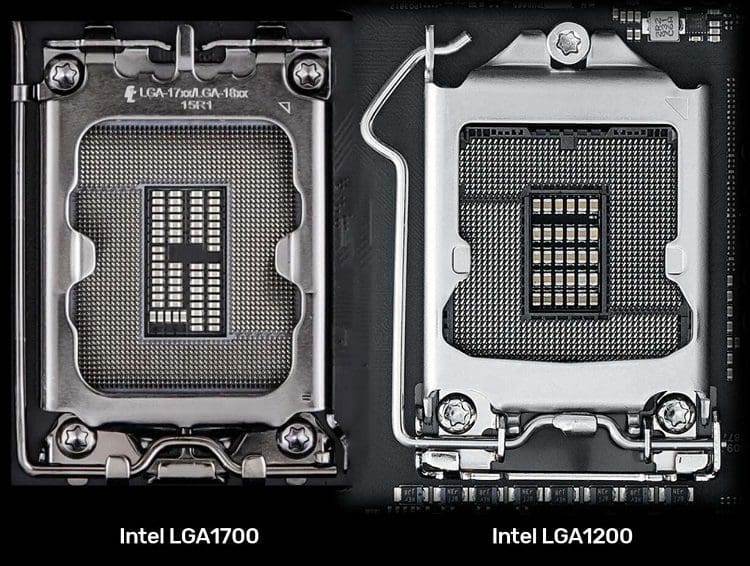
Unhelpfully, though CPU sockets tend to have unwieldy names such as LGA1700 or AM4.
Theres the same problem with chipsets too.
These two Intel sockets are fairly similar but completely incompatible.
It can be easy to miss the differences when theyre not side-by-side.
Conclusion
The motherboard is the spine of a computer, connecting everything together and enabling communication.
Care needs to be taken to ensure compatibility with the CPU.
The case should also be a compatibility consideration as motherboards come in a range of small and large sizes.