These networks are a lynchpin of modern communications, enabling communication between many devices.
The main addressing scheme used for the internet is known as IP or Internet Protocol addresses.
There are two IP address schemes in operation at the moment.
IPv4 is the traditional addressing scheme.
IPv6 is being rolled out as a replacement, as the IPV4 scheme has run out of usable addresses.
In this notation, each of the four numbers must be between 0 and 255.
A number of types of addresses are set aside as having a special meaning.
IPv6 addresses are more complicated to display.
They can be displayed with up to eight segments of up to four hexadecimal digits, separated by colons.
An example IPv6 address could look like this: fe80:4749:dadb:748d:ff:334c:ffff:f000.
As with IPv4 some address types are reserved for certain uses.
All IPv6 addresses that start with fe80 are local addresses with the same restrictions as local IPv4 addresses.
This is notation shorthand designed to make IPv6 addresses easier to read, write, and remember.
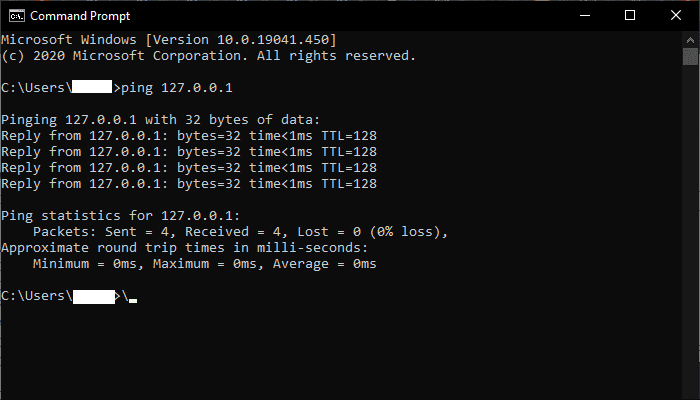
The loopback address
The Loopback address is another example of a reserved address.
In IPv4, the address 127.0.0.1 is supported by all devices as the loopback address.
In IPv6, the loopback address is ::1.
Only one address is allocated for use for loopback purposes.
Tip:The term localhost is reserved in the DNS scheme to refer to the loopback addresses.
Tip: it’s possible for you to also manually specify port numbers if youre hosting services on non-standard ports