HyperText Markup Language, or HTML, is the primary language for web pages on the internet.
The best example characters to use are the less than and greater than symbols.
Respectively these symbols are used to open and close code segments in HTML.
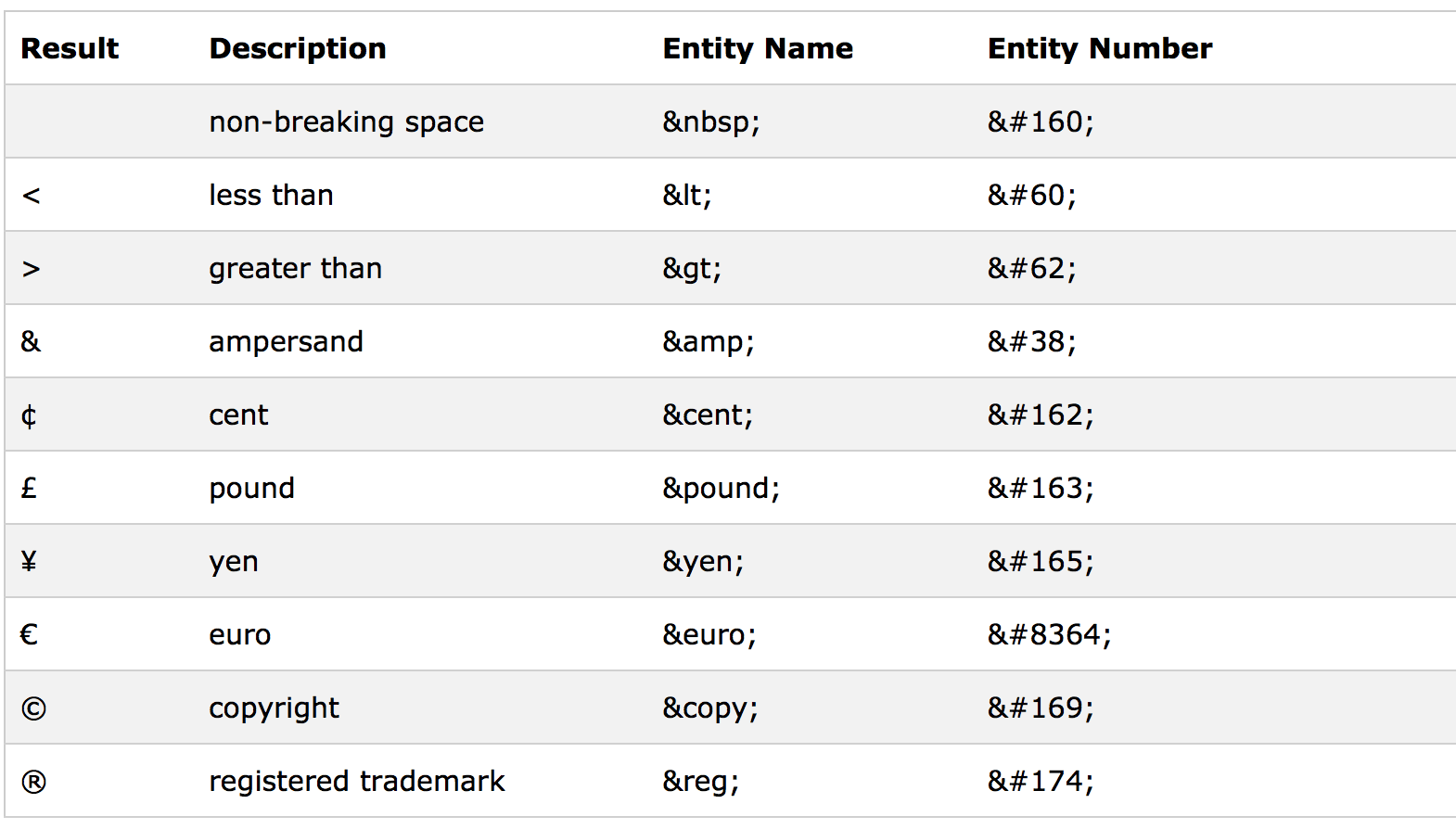
The correct method of printing these characters to the screen safely is to use HTML entities.
Unfortunately, many web developers forget that users can submit input to many websites.
Tip: Dont try submitting special characters to websites in an attempt to find XSS vulnerabilities.
All HTML entities start with an ampersand & and end with a semi-colon ;.
Most characters are identified by an entity number although some special characters have a shorthand name too.
The web client knows that these strings mean it needs to display the relevant characters.
In most cases, users should only ever see the characters that HTML entities represent.
This happens as the ampersand character appears in its own encoded version.